Title: Exploring the Top 5 CDN Magic Quadrant Leaders: Unraveling the Secrets to Their Success
Introduction
Have you ever wondered what makes a Content Delivery Network (CDN) stand out in the highly competitive world of network engineering? In this article, we will dive deep into the CDN Magic Quadrant to uncover the secret sauce behind the top 5 CDNs that have effectively conquered the digital landscape. Our aim is to provide you with an in-depth analysis and review of these prominent CDNs and enable you to make informed decisions for your businesses. So, let’s embark on this journey to unveil the mastery of the top 5 CDN Magic Quadrant leaders.
1. Akamai Technologies: Trailblazing CDN Performance and Security
Founded in 1998, Akamai Technologies sits at the pinnacle of the CDN Magic Quadrant due to its robust and comprehensive suite of CDN services. The company has consistently focused on bolstering its global infrastructure, currently boasting over 300,000 servers in 130 countries. Akamai’s Adaptive Media Delivery optimizes content delivery based on real-time network conditions, ensuring flawless online experiences.
Apart from exceptional performance, Akamai emphasizes security, offering integrated solutions such as Web Application Firewall (WAF) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection. This dual focus on performance and security makes Akamai a forerunner in the CDN Magic Quadrant.
2. Cloudflare: Redefining CDN Accessibility and Affordability
A relatively new player in the CDN Magic Quadrant, Cloudflare was founded in 2009 to provide easy-to-use, affordable CDN services to businesses of all sizes. With data centers in more than 200 locations, Cloudflare enables quick content delivery with minimal latency.
The company’s intuitive dashboard and simplified pricing structure have contributed to its popularity among developers and small-scale enterprises. Additionally, Cloudflare offers advanced features such as Argo Smart Routing, which improves performance by identifying and routing traffic along the fastest available paths.
3. Fastly: Empowering Real-Time CDN Customization
Fastly is a modern CDN provider that has gained traction in the CDN Magic Quadrant for its unique positioning based on near real-time configuration and cache control. By leveraging solid-state drives (SSDs) and strategically located Points of Presence (PoPs), Fastly minimizes latency and accelerates content delivery.
One significant distinguishing factor with Fastly is its focus on giving customers real-time control over their CDN configurations. Using Fastly’s powerful APIs and Instant Purge feature, organizations can achieve rapid update propagation, making it suitable for dynamic content and time-sensitive use cases.
4. Limelight Networks: Pioneering Low-Latency Video Streaming
Having entered the CDN Magic Quadrant in 2001, Limelight Networks has been synonymous with industry-leading live video streaming solutions. Limelight’s innovative Realtime Streaming technology reduces end-to-end latency to less than a second, enabling truly interactive and engaging experiences.
Apart from top-tier video delivery capabilities, Limelight provides advanced features such as multi-device media delivery, online video platform integration, and secure content delivery. Furthermore, their edge compute capabilities enable organizations to deploy serverless applications at the edge closer to end-users, enhancing response times and reducing operational costs.
5. Amazon CloudFront: Capitalizing on AWS Ecosystem Synergy
As part of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) ecosystem, Amazon CloudFront has secured its position in the CDN Magic Quadrant by offering seamless integration with AWS products and services. With over 220 PoPs across the globe, CloudFront ensures rapid content delivery and minimal latency.
The tight integration between CloudFront and AWS infrastructure allows customers to leverage additional services such as AWS Shield for DDoS protection, AWS WAF for application layer security, and AWS Lambda@Edge for serverless computing at the edge. Businesses deeply embedded in the AWS ecosystem will find Amazon CloudFront an ideal fit for their CDN requirements.
Conclusion
In this article, we have examined the top 5 CDN Magic Quadrant leaders and explored the key factors that have contributed to their success. To reiterate, the main elements contributing to a CDN’s effectiveness in the Magic Quadrant include performance, security, ease of use, customization, advanced features, and seamless integration with existing technology stacks.
When selecting a CDN, it is crucial to take these attributes into account while also considering your organization’s unique requirements and infrastructure. By doing so, you can make an informed decision that optimizes content delivery and maximizes user satisfaction, ensuring the long-term success of your business.
Diamond D3000N Super Discone Ultra-Wideband Antenna: Great for SDR and Scanners!
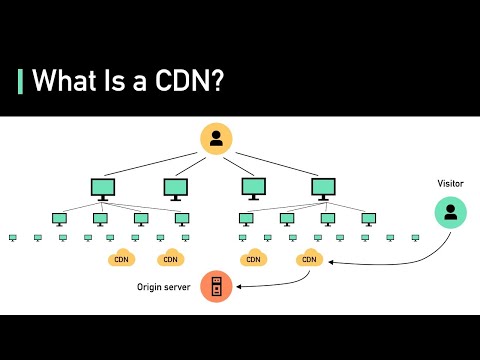
What Is A CDN? How Does It Work?
How does Akamai CDN work?
Akamai CDN, or Akamai Content Delivery Network, is a large distributed network of servers strategically placed across the globe. Its primary goal is to ensure fast, secure, and reliable delivery of Internet content. To understand how Akamai CDN works, let’s break down its core components and functions.
1. Edge Servers: Akamai CDN consists of thousands of these servers located in numerous data centers worldwide. These servers cache (store) and deliver web content, such as HTML pages, JavaScript files, images, and videos.
2. Content Caching: When a user requests web content, Akamai CDN caches the content on its edge servers closest to the user. This reduces the distance (latency) between the user and the content, resulting in faster load times.
3. Load Balancing: Akamai CDN uses load balancing algorithms to distribute incoming traffic evenly among its edge servers. This prevents any single server from becoming overwhelmed with too many requests, which could lead to slower load times or server failure.
4. Route Optimization: Akamai CDN constantly monitors the performance of the Internet and optimizes the path taken by the content to reach the end user. This ensures that the content is delivered quickly and efficiently, even during periods of high traffic or network congestion.
5. Security: Akamai CDN provides multiple layers of security to protect websites and content from cyber threats, such as Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, data breaches, and malicious bots. This includes Web Application Firewall (WAF) capabilities and advanced security features, such as bot management and API protection.
In summary, Akamai CDN works by caching, load balancing, route optimization, and providing security to deliver content quickly and efficiently to users worldwide. This results in improved website performance, user experiences, and protection against cyber threats for businesses using Akamai’s extensive CDN infrastructure.
What does a CDN cost?
The cost of a CDN, or Content Delivery Network, can vary significantly depending on the provider and the specific services and features you need. Generally, CDNs offer several pricing models including pay-as-you-go, fixed rate plans, and enterprise solutions.
Pay-as-you-go pricing typically charges based on the amount of data transferred (bandwidth consumed) and the number of requests made to the CDN. The cost per gigabyte (GB) usually decreases as your usage increases.
Fixed rate plans often include a set amount of bandwidth and requests per month, with additional fees for overages. These plans are suitable for businesses with predictable traffic patterns.
Enterprise solutions are tailored to the specific needs of large organizations and can include dedicated support, custom features, and negotiated pricing.
When considering the cost of a CDN, it’s important to evaluate the performance, reliability, and security of the service, which may impact the value you receive. Additional features such as geographic coverage, DDoS protection, and real-time analytics may also influence the total cost.
In summary, the cost of a CDN varies depending on your specific requirements and the provider you choose. It’s crucial to compare different offerings and pricing models to find the best solution for your needs.
What does CDN stand for?
In the context of content delivery networks, CDN stands for Content Delivery Network. It refers to a system of distributed servers that work together to provide fast and efficient delivery of internet content. This network helps improve speed and reliability for users accessing websites or applications by serving content from the nearest available server.
What is the world’s largest CDN provider?
The world’s largest CDN provider is Akamai Technologies. Akamai has a massive global network and delivers a significant portion of the world’s web traffic through its Content Delivery Network (CDN) infrastructure.
What are the top three CDN providers in the most recent Gartner Magic Quadrant for Content Delivery Networks?
The most recent Gartner Magic Quadrant for Content Delivery Networks ranks the top three CDN providers as Akamai Technologies, Cloudflare, and Fastly. These companies have been recognized for their significant impact, service offerings, and performance in the content delivery network industry.
How has the CDN landscape evolved according to the Gartner Magic Quadrant over the past few years, and what trends can we expect in the future?
Over the past few years, the CDN landscape has evolved significantly according to the Gartner Magic Quadrant, with several key trends becoming more prominent. To understand these shifts, it’s important to consider the four categories in the Magic Quadrant: Leaders, Challengers, Visionaries, and Niche Players.
1. Consolidation and growth in Leaders: In recent years, we have seen a clear consolidation of major CDN companies like Akamai, Fastly, and Cloudflare moving towards the “Leaders” quadrant. These companies have expanded their product portfolios, increased their global scale, and improved the overall quality of their services to stay ahead in the market.
2. Emergence of new Challengers and Visionaries: The CDN landscape has also witnessed the rise of new Challengers and Visionaries such as Limelight Networks and StackPath. These companies are pushing the boundaries in terms of technology and delivering innovative solutions that cater to the ever-growing demand for content distribution.
3. Increasing focus on security: As cyber threats continue to escalate, CDN providers have increasingly started to emphasize security measures to protect their customers’ content and infrastructure. This includes offering DDoS protection, Web Application Firewalls (WAF), and TLS encryption as key components of their content delivery services.
4. Edge computing and serverless computing: The increasing prevalence of edge computing and serverless computing has led to CDNs developing solutions capable of running compute functions closer to end users. This minimizes latency, improves performance, and reduces the load on origin servers.
5. Multi-CDN strategies: To ensure high availability, performance, and redundancy, many businesses are adopting multi-CDN strategies, where they use a combination of different CDNs to deliver content. This trend is expected to grow in the future, as businesses seek to optimize their content delivery infrastructure.
6. Expanding market segments: CDNs are no longer just for large enterprises and content providers. With the increase in streaming services, gaming platforms, and e-commerce applications, CDN services are also catering to small and medium-sized businesses, further expanding the market.
Moving forward, we can expect several trends to shape the future of the CDN landscape:
1. 5G and IoT: The deployment of 5G networks and the growth of Internet of Things (IoT) devices will further increase the demand for more efficient and scalable CDNs, as well as contribute to the overall growth of the market.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): As technologies advance, AI and ML will help CDN providers optimize traffic routing, edge computing capabilities, and security measures, leading to better performance and reliability.
3. New entrants and competition: With the market growing rapidly, we can anticipate more players entering the CDN space, resulting in increased competition and innovation in the sector.
In conclusion, the CDN landscape has evolved significantly over the past few years according to the Gartner Magic Quadrant, with major players like Akamai, Fastly, and Cloudflare taking the lead while new Challengers and Visionaries enter the market. Moving forward, we can expect emerging technologies and an expanding customer base to continue shaping this dynamic industry.
What criteria does Gartner use to evaluate and rank CDN providers in their Magic Quadrant report?
Gartner utilizes a variety of criteria to evaluate and rank CDN providers in their Magic Quadrant report. These criteria are grouped into two main categories: Ability to Execute and Completeness of Vision. Some key factors within these categories include:
1. Product or Service: Gartner assesses the core goods and services provided by each vendor, their overall functionality, quality, and performance. This includes evaluating how well the CDN meets customer requirements and integrates with other technology platforms and systems.
2. Overall Viability: This factor looks at the financial health of the vendor, such as revenue growth and profitability, as well as organizational and management stability. It’s crucial for a CDN provider to have adequate resources and support to maintain and develop their business.
3. Sales Execution/Pricing: Gartner analyzes the effectiveness of each vendor’s sales processes, channels, and pricing models. A competitive pricing strategy and strong sales execution can contribute to the success of the CDN provider.
4. Market Responsiveness/Record: This criterion evaluates the vendor’s ability to respond to market changes and customer needs, as well as their track record of delivering on their commitments. A CDN provider with a history of adapting quickly to market demands and keeping up with industry trends is more likely to succeed.
5. Marketing Execution: Gartner examines the clarity, quality, and effectiveness of each vendor’s marketing programs, campaigns, and communications. A CDN provider with strong marketing execution can generate better awareness and customer interest in their products and services.
6. Customer Experience: This factor assesses the overall customer experience, including ease of deployment, product reliability, quality of technical support, and responsiveness to issues. A CDN provider that offers a positive customer experience is more likely to retain and attract new clients.
7. Operations: Gartner evaluates the efficiency and effectiveness of each vendor’s operational processes, including service delivery, support, sales, and marketing operations. A CDN provider with well-managed operations can deliver consistent results and maintain high service levels.
8. Market Understanding: This criterion looks at the vendor’s understanding of customer needs, market dynamics, and industry trends. A CDN provider with a deep understanding of the market is more likely to develop innovative solutions that address emerging customer requirements.
9. Offering (Product) Strategy: Gartner assesses the vendor’s approach to product development, including their roadmap and plans for future enhancements. A CDN provider with a clear and compelling product strategy is more likely to maintain a competitive edge in the market.
10. Business Model: This factor examines the soundness and general effectiveness of the business model used by the vendor. A well-structured and sustainable business model can contribute to the long-term success of the CDN provider.
By considering these factors and criteria, Gartner produces a comprehensive evaluation of CDN providers in their Magic Quadrant report, ultimately ranking them based on their ability to execute and completeness of vision.